Understanding the Importance of CT Scan for Lung Cancer
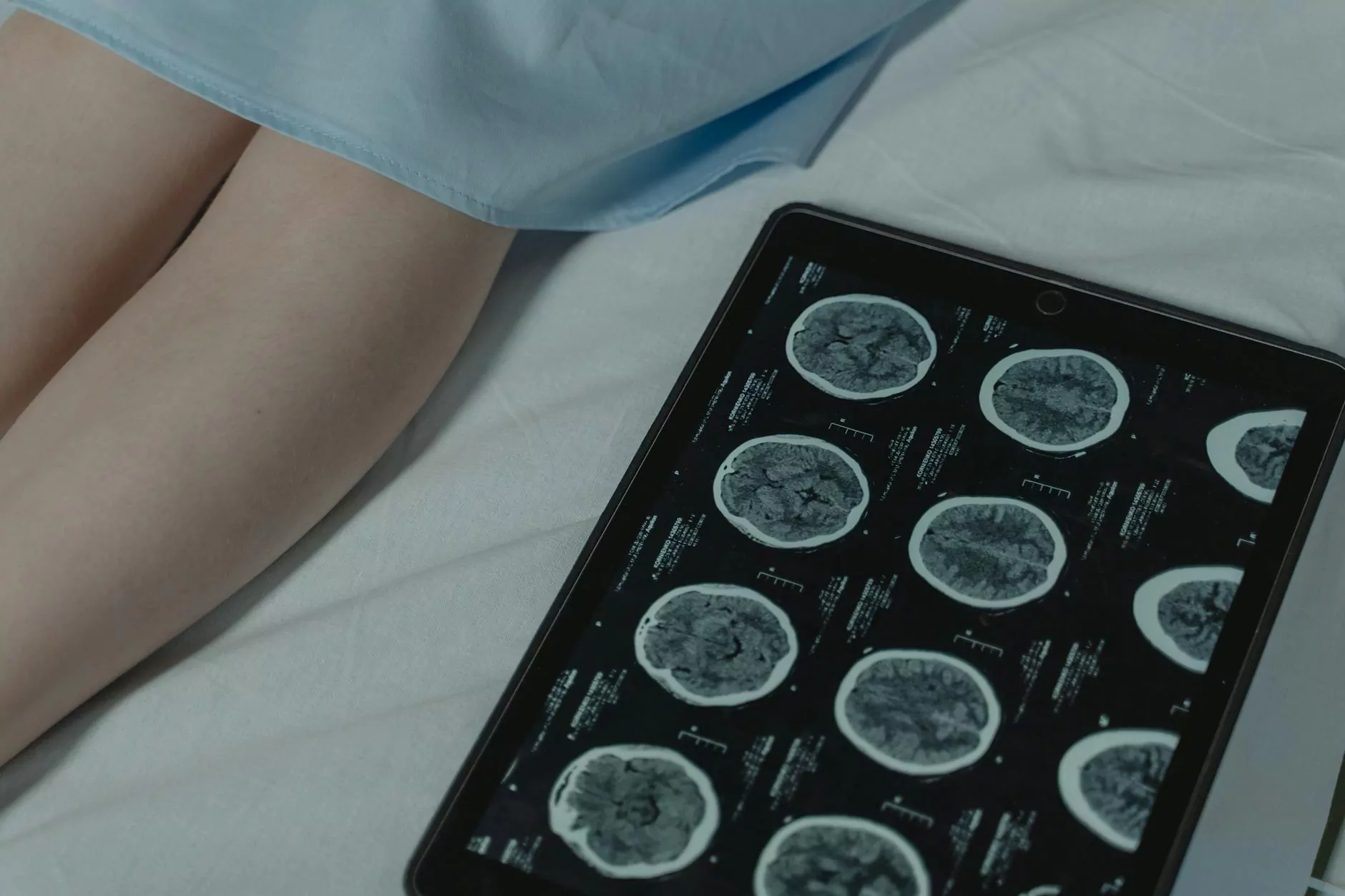
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers around the world, responsible for a significant number of cancer deaths each year. Early detection is critical for improving outcomes and increasing survival rates. The CT scan for lung cancer has emerged as a vital tool in the early diagnosis and management of this disease. This comprehensive guide will explore what CT scans are, their advantages, and their critical role in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan, or Computed Tomography scan, is a sophisticated imaging technique that utilizes x-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Unlike regular x-rays, CT scans provide a more comprehensive view of internal structures. This makes them particularly useful in examining complex areas like the lungs.
Why is a CT Scan Important for Lung Cancer?
The role of a CT scan in lung cancer cannot be overstated. Here are some key benefits:
- Early Detection: CT scans can identify lung tumors before they are visible through conventional x-rays, significantly increasing the chances of successful treatment.
- Detailed Imaging: The high-resolution images generated by CT scans allow for better visualization of lung anatomy, helping in distinguishing between cancerous and non-cancerous lesions.
- Staging Cancer: CT scans are crucial in determining the stage of lung cancer, which assists doctors in crafting the most effective treatment plans.
- Monitoring Treatment: After treatment, CT scans are often used to monitor the effectiveness of therapy and check for recurrence.
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to biopsies, CT scans are non-invasive and carry less risk, making them a safer screening option.
Who Should Get a CT Scan for Lung Cancer?
Not everyone requires a CT scan, but certain high-risk groups should consider regular screening:
- Individuals aged 55 to 80 years with a significant smoking history (30 pack-years or more).
- People who have quit smoking within the past 15 years.
- Individuals with a family history of lung cancer or known genetic predispositions.
- Those who have been exposed to known carcinogens, such as firefighters or asbestos workers.
The Procedure: What to Expect During a CT Scan
Understanding the CT scan procedure can help alleviate apprehensions. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of what patients can expect:
- Preparation: Patients may need to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan. Informing the doctor about any allergies, especially to contrast dye, is important.
- Arrival: Patients check in at the imaging center and undergo a brief consultation with a technologist who will explain the process.
- Positioning: The patient will lie on a narrow table that slides into the CT scanner—a large machine shaped like a doughnut.
- Scanning: As the table moves through the scanner, the machine takes a series of x-ray images from different angles. The process is quick, usually taking about 10 to 15 minutes.
- Post-Procedure: After the scan, patients can resume normal activities immediately. The results will be analyzed by a radiologist and typically discussed with the patient in a follow-up appointment.
Understanding the Results: Can CT Scans Detect Lung Cancer?
CT scans can reveal abnormalities such as nodules or masses in the lungs that may indicate cancer. However, it's essential to understand that:
- Not Every Nodule is Cancerous: Many lung nodules are benign and do not require treatment.
- Further Testing: If abnormalities are found, additional imaging or biopsy may be necessary to make a definitive diagnosis.
- Risk of False Positives: Some non-cancerous conditions can appear suspicious on a CT scan, leading to unnecessary worry and further testing.
Advancements in CT Imaging for Lung Cancer
The field of medical imaging is continually evolving, leading to advancements in how lung cancer is diagnosed and monitored. Some recent innovations include:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: These scans reduce radiation exposure while still providing high-quality images, making them safer for regular screening.
- 3D Imaging Techniques: Enhanced visualizations can help doctors better plan surgical procedures and treatment strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms are being utilized to analyze CT scans more accurately, improving diagnostic capabilities and outcomes.
Treatment Options Following a CT Scan Diagnosis
After a diagnosis of lung cancer, treatment options vary based on the type and stage of cancer:
Surgery
In cases of localized cancer, surgical removal of the tumor may be the preferred approach. The type of surgery will depend on the tumor's size and location.
Radiation Therapy
This treatment uses high energy rays to kill or shrink cancer cells and may be used in conjunction with surgery or as a primary treatment for non-operable tumors.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy employs drugs to destroy cancer cells and is often used for more advanced cancer stages or when surgery isn't feasible.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies utilize drugs that specifically attack cancerous cells with specific genetic markers, offering a more personalized approach to treatment.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy enhances the body’s natural defenses against cancer, offering new hope for patients, especially in advanced stages of the disease.
Conclusion: The Future of Lung Cancer Detection and Treatment
In conclusion, the CT scan for lung cancer is an invaluable tool in the early detection and management of this serious disease. Understanding the benefits, processes, and potential advancements in technology underscores the importance of imaging as part of a comprehensive approach to lung health. At HelloPhysio, we are committed to providing insightful resources and quality care in the fields of Health & Medical, Sports Medicine, and Physical Therapy. Continued research and innovations in imaging and treatment methodologies will pave the way for more effective strategies against lung cancer in the future.